Get imagery but it raises the ole question; not all... but why do women look funny throwing a ball?
It’s in the DNA somehow.
Get imagery but it raises the ole question; not all... but why do women look funny throwing a ball?
It’s in the DNA somehow.

Biological sex differences: bones & musclesMaybe it has to do with their upper body muscle structure? I don't know enough about muscle or bone structure differences between the sexes but my guess is something like that, unless boobs get in the way somehow.
 Male & female skeletons – sexual dimorphism
Male & female skeletons – sexual dimorphism
| Highest Male Record Below Women’s Maximum | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Event | Sex | Achieved | Name | Category |
| Olympic Records in Weight Lifting – Maximum Lifts | |||||
| 2012 | Snatch | F | 151kg | Tatiana Kashirina | 75kg+ |
| 2012 | Clean & Jerk | F | 187kg | Zhou Lulu | 75kg+ |
| 2012 | Total | F | 333kg | Zhou Lulu | 75kg+ |
| 2016 | Snatch | M | 216kg | Behdad Salimi | 105kg+ |
| 2004 | Clean & Jerk | M | 263kg | Hossein Rezazadeh | 105kg+ |
| 2016 | Total | M | 473kg | Lasha Talakhadze | 105kg+ |
| 2000 | Snatch | M | 138kg | Halil Mutlu | < 56kg |
| 2012 | Clean & Jerk | M | 177kg | Óscar Figueroa | < 62kg |
| 2012 | Total | M | 327kg | Kim Un-guk | < 62kg |
 Women have more Type 1 (slow-twitch) fibres, and use them better
Women have more Type 1 (slow-twitch) fibres, and use them better Well, duh, that’s why we have biological sexes
Well, duh, that’s why we have biological sexes
Biological sex differences: bones & muscles
7th July 2017 by FPFW

Women know all about being ‘born in the wrong body’.
It is the biological sex of our bodies that is at the root of the sexism women have to deal with throughout life. It is why we are at risk of sexual and physical violence from males. It is why women are expected to take on caring roles throughout life. It is why we are paid less at work. It is why women’s sports aren’t valued like men’s are. It is why we have to fight daily against the sex stereotypes society imposes on us.
It is also why women have fought hard for female-only spaces, female-only prisons, female-only opportunities and female-only competitive sports. We are different to males and ignoring that difference ignores the lived experience and needs of females. Equality of opportunity is about treating everyone fairly, not the same.
More and more males are now choosing to ‘live in role as women’. But they can’t actually BE FEMALE. It’s a medical impossibility. There is not such thing as a ‘sex change’. This is simple fact, not prejudice or transphobia. Biological sex affects every part of us, down to the cellular level. Our biological sex informs our bodily structure & function, metabolic processes, and health outcomes. Yet you could be forgiven for thinking women are just like men with boobs and an extra hole! The internet’s full of misinformed nonsense – and, worryingly, even medical science doesn’t know the half of it.
Quick links in this post: skeleton | head | muscles | reproductive | ligaments | conclusion |
Next post: chromosomes & biological sex
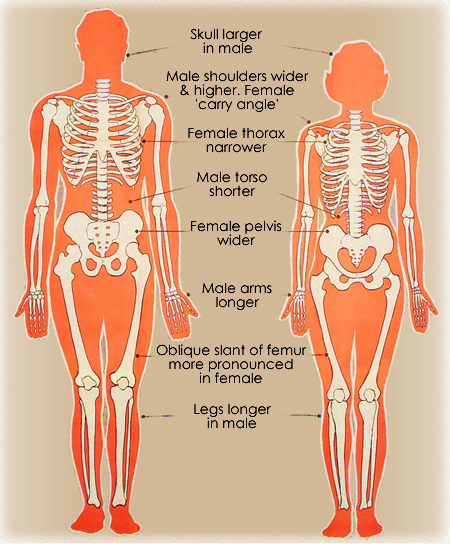
What are the differences between male and female skeletons?
WOMEN ARE SHORTER, about 9% on average. Nigerians have the smallest recorded height difference between the sexes at 4%, while men of the UAE are 11% taller than their women.
MALE BONES ARE BIGGER AND STRONGER, in both size and density. Peak male bone mass is around 50% more than women’s, and women lose bone faster as we age. Black people have significantly stronger bones than whites: black women’s peak bone mass is the same as white men’s.
WOMEN AND MEN HAVE THE SAME NUMBER OF RIBS. We have 12 pairs, though some people are born with 11 or 13 pairs to no ill effect.
MEN HAVE BIGGER HEADS AND LONGER ARMS AND LEGS than women, relative to body size. Sources differ on comparative limb length but they all agree women have smaller, lighter heads & necks. Did you know a human head weighs about 5kg?
The biological sex of an adult skeleton can be determined with 95% accuracy by measuring the hip bones alone, 83% accuracy by the skull, and 80% accuracy by the long bones (femur & tibia).
Male & female skeletons – sexual dimorphism
WOMENS ELBOWS AND SHOULDERS are slightly different from men’s. Our arms bend a little further from our bodies and are more mobile at both joints.
FINGER LENGTH: Greater exposure to androgens in utero leads to a 4th (ring) finger that is longer than the 2nd (index), as often seen in men.
WOMEN HAVE A LONGER TORSO. Our skeleton accommodates extra reproductive organs and finds space to push things out of the way during pregnancy. It makes our legs shorter than men’s.
THE LARGER FEMALE PELVIS is better adapted for childbirth. It’s wider, longer, and held together by ligaments that soften during pregnancy, allowing the two halves to slide apart because of their narrow pelvis. Women’s slanted thigh bones put extra pressure on the knee joints, which have to rotate while men’s do not.
Differences Between Male and Female Heads
MEN HAVE BIGGER BRAINS by more than 10% relative to body size. Women’s brains have more connections between the two hemispheres, using both sides of the brain much more often than men.
Men’s brains are bigger, but there’s no IQ advantage
WOMEN’S SKULLS ARE THICKER by 10% but men tend to have a bony ridge on the brow line and a heavier jaw. The male forehead is likely to slope backwards; women’s are more vertical.
ESTROGEN CORRELATES with higher eyebrows, fuller lips, and a rounder jawlinewith a more pointed chin.
TESTOSTERONE CORRELATES with a square chin & sharply angled mandible, a more prominent Adam’s Apple, more facial hair and male-pattern baldness with age.
EYESIGHT:: Women’s colour perception and peripheral vision are better than men’s. Men do better on long distance focus. These may be evolutionary adaptations for childcare and hunting, respectively.
HEARING Women have much better high-frequency hearing; we’re particularly well adapted to identify a baby’s cry – this stretches to kittens and other young animals. However, we lose even more low-frequency hearing with age.
VOICE: Men’s (usually) deeper voices are the result of growth in the vocal tract and vocal folds at puberty.
Is There A Difference Between Male and Female Muscles?
women are around 30-35% muscle by weight, while men are 40-50% muscle. This varies a lot by age, health, fitness, body type and genetics. Any averagely healthy person can build more muscle by exercising and, to an extent, change the composition of their muscles. But women can’t match the bulk or strength of men’s skeletal muscles – unless they artificially raise their androgens by a significant amount, which would be dangerous.
EAST GERMANY’S vicious programme of treating young athletes with steroids won many medals, but at tremendous human cost. Hormone doping scandals continue to shake the sporting world, along with confusion over natural variations in biological sex and transgender medications. The only clear lesson to be drawn from this is that Testosterone enhances muscle growth & strength.
IT’S UNFASHIONABLE to say women can’t build strength & muscles like men – but it is demonstrably true, so I think it worth offering a little evidence.

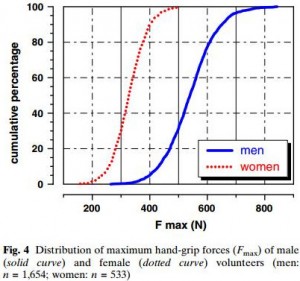
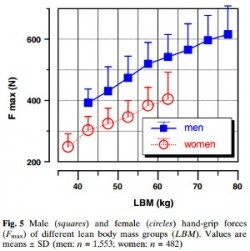
Hand grip is one of the most widely-used markers for strength. The strongest 10% of females can only beat the bottom 10% of men! Weight for weight (lean body mass only), women’s grip remains pretty feeble compared to the men. These were large samples that included plenty of fit, young sportswomen with good upper body strength. Taking the 60 elite women separately, they were still only as good as an average to weak man.
In Olympic weightlifting, the biggest total weight achieved by a woman was 333kg by Zhou Lulu in the heaviest women’s body weight category, 75kg+. She also won the Clean & Jerk with 187kg, while Tatiana Kashirina lifted 151kg in the snatch.
Date Event Sex Achieved Name Category Highest Male Record Below Women’s Maximum Olympic Records in Weight Lifting – Maximum Lifts 2012 Snatch F 151kg Tatiana Kashirina 75kg+ 2012 Clean & Jerk F 187kg Zhou Lulu 75kg+ 2012 Total F 333kg Zhou Lulu 75kg+ 2016 Snatch M 216kg Behdad Salimi 105kg+ 2004 Clean & Jerk M 263kg Hossein Rezazadeh 105kg+ 2016 Total M 473kg Lasha Talakhadze 105kg+ 2000 Snatch M 138kg Halil Mutlu < 56kg 2012 Clean & Jerk M 177kg Óscar Figueroa < 62kg 2012 Total M 327kg Kim Un-guk < 62kg
You have to go down to men under 62kg to find a champion Zhou Lulu could beat, and under 56kg for a male champion Tatiana Kashirina could beat in the Snatch. Women of less than 75kg couldn’t beat any of the male winners, not even the smallest men.
INTENSIVE RESISTANCE TRAINING can elevate steroid secretion in both males & females but, as seen above, we’re simply not built for the muscular bulk and explosive strength of those who were born with a Y chromosome – and the female limit is a long, long way behind the male maximum.
MEN HAVE MASSIVE UPPER BODY STRENGTH ADVANTAGE, but women do (somewhat) better with our lower-body muscles. Females generally have 40% less skeletal muscle than males on the top half; 33% less below the waist. These data are often wrongly reported – it means men have 66% more upper-body muscle than women, and 50% more lower-body muscle.
MEN ALSO HAVE LOWER BODY STRENGTH ADVANTAGE. A 70kg elite male athlete can squat 35% more weight than a 70kg elite female; this goes up to 57% more when both athletes are 120kg.
MEN’S MUSCLES ARE MORE SOLID, due to a higher proportion of Type 2 fast-twitch fibres. This type of muscle fibre contains a lot of protein but not much blood. It can expand/contract rapidly with great force and generate its own energy, but it draws on the rest of the body for oxygen. Because of this, Type 2 muscle fibres get tired more quickly. Although it varies by body type & genetics, men’s muscles are, proportionally, about 50% more Type 2 than women’s.
Women have more Type 1 (slow-twitch) fibres, and use them better
WOMEN’S TYPE 1 MUSCLE FIBRES PROTECT HEALTH. Type 1 (slow-twitch) fibres are more loosely packed and have their own capillaries. This means they can keep going for a long time. They interact with other metabolic processes, which helps to protect against insulin resistance and heart disease, supports the immune system and promotes hormonal functions.
WOMEN ACTIVATE BOTH TYPES OF FIBRE. Olympic athletes aside, both female & male bodies use Type 1 fibres first, then shift to Type 2 when those get fatigued – but women have been found to switch between the two throughout exertion. This is the secret of our famed endurance: not the slow-twitch fibres themselves, but neuromuscular activity which uses all the fibres.
WOMEN ARE 90% AS FAST AS MEN. Across all speed events, women consistently achieve 90% of the men’s speeds. This seems to be where our multi-tasking muscle fibres come good, but they still can’t close that 10% gap.
MUSCLES OF THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. You don’t see much about them in the fitness blogs, do you?! These incredible organs are lined with muscles so powerful that they can squeeze a baby out, and so elastic that they can stretch to accommodate the baby & placenta, etc, while holding them safe – and then return to shape.
THE VAGINA is not a ‘hole’. It’s a muscular tube connecting internal organs to the outside world. Around the mucosal lining is a folded layer of smooth muscle. Another layer wraps lengthways around that, so the vagina can stretch & hold in all directions.
THE UTERUS is a thick-walled muscular organ with no fewer than three layers of folded muscles going in different directions. Together, they’re called the myometrium.
MEN DON’T HAVE any such awesome muscles in their reproductive organs. They feel strong contractions during orgasm, as women do, but theirs are localised bursts while our whole uterus & vagina contract in waves – more often and for longer, if we’re lucky.
Ligaments
WOMEN’S ARE THINNER AND SOFTER than men’s – apart from around our reproductive organs, where they can be phenomenally strong and elastic. At puberty our ligaments become “lax” compared to men’s. This would seem to be a hormonal effect designed to facilitate separation of the pelvic bones for childbirth – pity it weakens all of the ligaments all of the time, as our “laxity” causes joint instability. It’s responsible for a high number of sporting injuries.
WOMEN ARE MORE FLEXIBLE, due to that same laxity.
WOMEN’S BACKS HAVE TO SUPPORT THE WEIGHT OF BREASTS. This gave one bicycle designer a headache, and is the reason for women’s ubiquitous lower back pain.
Conclusion
IT’S ALL ABOUT REPRODUCTION.
Well, duh, that’s why we have biological sexes
NATURE DOESN’T CARE who works at the office/factory, who can fight the hardest or how many different tasks a person can do. Nature doesn’t care if your back hurts. Nature doesn’t care if men get diabetes and have heart attacks, or if women’s bones break in later life. All nature cares about is propagating the species – it doesn’t even matter if most of the young die (look at turtles!) As long as a species has more than enough young to replace itself, and keeps those young alive long enough to reproduce themselves, it’s a job well done as far as nature cares.
Humans are very, very successful in this respect.
WOMEN ARE NOT WEAK. Like all other mammals, we need a female sex and a male sex because that’s how we keep the species going. Females sacrifice some physical force in favour of reproductive fitness, because it takes a hell of a lot of specialised strength & stamina to gestate, birth and nurture young mammals. As it goes, women have evolved compensatory strategies (some on this page, more in later posts!) This is a spectacular testament to the all-round power & awesomeness of women … and of men. When we work as a team, we’re unstoppable.
WOMEN ARE NOT THE WEAKER SEX, JUST DIFFERENT. Blokes aren’t built to grow live human beings out of their own body tissues, recover almost immediately and spend the next year feeding said infant with their own bodily fluid. They’re male. Women are definitely weak when judged against male bone & muscle performance – but you try judging males against the female performance. It is strange that we’ve defined physical strength & weakness in terms of what men’s bodies can do … but that’s patriarchy, I guess!

Differences between male and female skeletons, heads and muscles
Is sex binary? Overview of the far-reaching differences between male & female bodies. Biological sex goes right down to the cellular level...fairplayforwomen.com

*SalmaSelma Hayek above btw
I couldn't resist...but, here goes with my very 1st boobies post!
Get imagery but it raises the ole question; not all... but why do women look funny throwing a ball?
It’s in the DNA somehow.

I couldn't resist...but, here goes with my very 1st boobies post!
I couldn't resist...but, here goes with my very 1st boobies post!
A woman can be sexy without flaunting it. Yeah I'm old school because artificially augmented via implant or hormonal just doesn't do it for me. I took this when we were 25 a long time ago obviously. Before the days of implants and other artificial augmentation.
View attachment 29974
